The effect of
consumption of Agaricus blazei edible mushroom on caspase2 gene expression in
hepatitis C patients using system biology and microarray data
Alireza
Panahi 1 *, Gholamreza Dadashi Oranj 2
1 Department of Biology, Faculty of
Sciences, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran
2 Department of Production Engineering and
Plant Genetics, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, University of Mohaghegh
Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran
*Corresponding Author: Alireza Panahi
* Email: arpanahi@uma.ac.ir
Abstract
Introduction: Agaricus blazei mushroom is used as a food and medicine, its effective
composition is beta-glucan, which is used to treat some cancers and infections,
including hepatitis C.Hepatitis C is an inflammatory disease that causes liver
necrosis. Caspase2 protein is one of the factors promoting cell apoptosis and
plays a role in tumor suppression. The purpose of this study is to determine
the expression changes of the caspase2 gene and its effects on liver cancer.
Materials
and Methods: In this project, raw expression data was obtained from the NCBI
(National Center for Biotechnology Information) GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus)
database section and using bioinformatics tools and methods and system biology
such as Matlab (An abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory), GEOR2 (Online
software) and Cytoscape, the effect of consuming the desired mushroom on
caspase2 gene expression was investigated.
Results: It was found that the beta-glucan combination has an increasing effect
on target gene expression (p-value=0.05692).
Conclusion: The results show that the beta-glucan present in the mushroom can play
a role as a prevention and even treatment of liver cancer by increasing the
expression of caspase 2 protein by directing the damaged cell towards
apoptosis.
Keywords: Beta-glucan, Agaricus blazei, hepatitis C, caspase2, Microarray,
System biology
Introduction
Agaricus
blazei belongs to the category of basidiomycetes or umbrella mushrooms, which
is one of the food items on people's tables in most countries. This mushroom is
mostly native to Brazil and Japan and is currently used as one of the edible
and medicinal mushrooms that are traditionally used to treat many common
diseases such as arteriosclerosis, hepatitis, blood lipids, diabetes, and
cancer. This mushroom also has immunomodulatory and anti-mutagenic properties (1). One of the most important effective compounds in edible
mushrooms Agaricus blazei is a beta-glucan polysaccharide (2,3). This type of
mushroom and even different types of edible mushrooms are used to treat some
cancers and infections, including hepatitis C, due to the presence of
beta-glucan polysaccharide (4). Hepatitis C is a type of
contagious infection that mainly affects the liver and is caused by a virus
that attacks the liver and causes inflammation of the liver (5). Most people infected with the hepatitis
C virus do not feel any symptoms, in fact, many of them may not even know that
this virus is present in their body (6). Hepatitis C can be chronic or
acute. Acute hepatitis C is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6
months of being infected with this virus and lasts for a few weeks. In most
people, acute hepatitis C turns into chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C
is a long-term disease and occurs when the hepatitis C virus remains in the
body for a long time (7). Hepatitis C virus infection can
cause serious liver problems such as liver cirrhosis or liver cancer (8). Caspase 2 protein is one of the
tumor suppressors. Caspase 2 may be an important protector against
tumorigenesis (9). A hallmark of tumorigenesis is
that cancer cells avoid apoptosis, so caspase 2 may suppress tumors by inducing
apoptosis of potential tumor cells. Alternatively, caspase-2 protein may
suppress tumor growth by inducing cell cycle arrest (10). In addition, it has been observed
that caspase 2 causes cell cycle arrest after DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
damage (11). Microarray is one of the most widely used methods of
generating Big data related to gene expression levels in genome function
projects (12). One of the best storage databases
is the GEO gene expression data set, which is located in the NCBI. In this
research, to investigate the increasing or decreasing effect of beta-glucan
consumption on caspase 2 gene expression, the gene expression data of the
project with accession number Gse3983, which is available in the NCBI database
as raw data, was used. Therefore, in order to find out the effect of beta-glucan
on increasing or decreasing the expression of the studied gene, the raw data of
the microarray has been measured and analyzed with bioinformatics software.
Materials and Methods
To get the data related to the expression of the caspase2 gene, refer
to the research carried out under the name of Gse3983, which was conducted on
four patients. These patients included three male and one female. The patients
(3 males one female, 48-56 years) had chronic hepatitis C infections that did
not respond to interferon/ribavirin treatment. They were given one week of treatment
with Agaricus extract (Gold Label from ACE Co, Japan, 20 ml 3x daily). Blood
samples were drawn before and after treatment. In order to investigate the
effect, we examined the changes of gene expression caused by the extract on a
human monocyte cell line (THP-1). Changes in the levels of mRNA transcripts
were measured using 35k microarrays (13). Microarray experiments provide the scientific community
with huge amounts of data. Without appropriate methodologies and tools,
significant information and knowledge hidden in these data may not be
discovered. Therefore, there is a need for methods capable of handling and
exploring big data sets. The field of data mining and machine learning provides
a wealth of methodologies and tools for analyzing large data sets (14). The raw data of this research has been presented in NCBI. The raw
data of the caspase2 gene has been published among thousands of genes that were
the result of microarray operations. By referring to the NCBI website and after
receiving the raw data from the GEO data sets section for pre-processing the
data, analysis and to determine the desired gene expression, MATLAB software
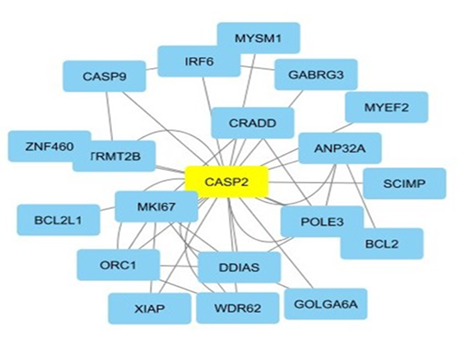
was used, and Cytoscape software were used to show the relationships of genes
in terms of genetic relationships with other genes. Also, GEO2R has been used
to analyze the data and examine the changes in the desired gene expression in
two groups of patients, i.e., a group of four patients before and after
treatment. Matlab is a programming and numeric computing platform used by
millions of engineers and scientists to analyze data, develop algorithms, and
create models. Using toolbox functions of matlab, we can read genomic and
proteomic data from standard file formats such as SAM, FASTA, CEL, and CDF, as
well as from online databases such as the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus and
GenBank. Cytoscape is an open-source software project for integrating
biomolecular interaction networks with high-throughput expression data and
other molecular states into a unified conceptual framework. GEO2R is an
interactive web tool that allows users to compare two or more groups of Samples
in a GEO Series in order to identify genes that are differentially expressed
across experimental conditions. In this study, MATLAB R2018A and Sytoscape
3.10.0 were used.
Results
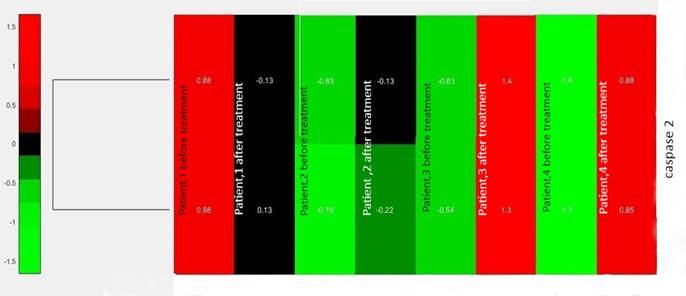
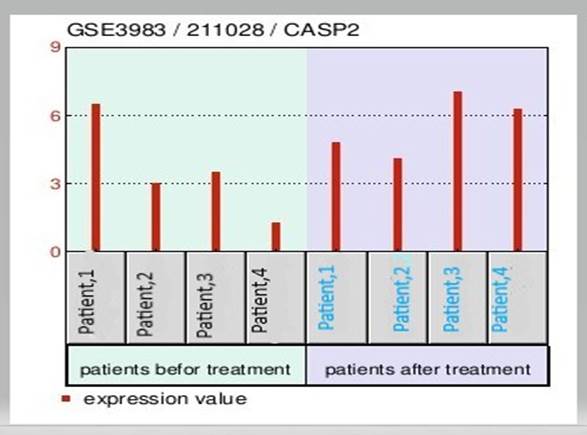
By
executing the command codes in the MatlabR2018a software, the clustergram of figure
1 was obtained.
Discussion
Beta-glucan is one of the natural polysaccharides found as a component
of the cell wall in grains, algae or in some microorganisms such as bacteria,
fungi and yeasts, and by examining beta-glucan in the 1960s and 1970s,
researchers well established the important role of beta-glucan in The immune
system has been proven to treat cancer, infection, and repair damaged bone
marrow (4). Hepatitis C is an inflammatory
liver necrosis disease that occurs acutely and chronically. The causative agent
of the disease is a virus from the flavivirus family and has a high tendency to
reproduce in liver tissue (7). Currently, about 170 million
people in the world have chronic hepatitis (8). 7 to 20% of these patients suffer
from liver cirrhosis (7). On the other hand, cirrhosis
causes serious complications such as liver cancer (15). Today, it is known that caspase 2
is the most important member of apoptosis and the coordinator of the death
pathway or the activation of other caspases (9). And the defect in the process of
apoptosis is the cause of many diseases including cancer (16). Caspase 2 is one of the tumor
suppressors and recent studies show that caspase 2 may play a role in
suppressing tumorigenesis (9). Caspase 2 protein expression
strongly localizes to injured/ballooned hepatocytes (17). Caspases mediate cell apoptosis
after stimulation; they can be divided into initiators of apoptosis, such as
caspase 2, 8, 9, 10, and 12, and effectors of apoptosis, such as caspase-3, 6,
and 7 (18). the present study, it was shown
that beta-glucan present in edible mushroom Agaricus balzei increased the
expression of caspase 2 protein. Therefore, caspase 2 may suppress tumors by
inducing apoptosis of potential tumor cells (10). Considering that caspases play an essential role during cell death
and changes in caspases are involved in the development of human cancer (19). on the other hand, in a study
conducted on gastric cancer by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray
approach, it was determined that the expression of Caspase 2 gene has changed
and these changes are reduced in gastric cancer cells compared to normal cells (17). Therefore, it can be said that the
beta-glucan present in the edible mushroom Agaricus blazei can increase the
expression of caspase-2 protein and thereby lead the damaged liver cells in
hepatitis C patients to apoptosis. In the end, it is suggested that the effect of beta-gluganan be
done in a laboratory and real-time PCR method on patients with hepatitis C
disease and the results be compared with the results of the research.
Conclusions
Therefore, according to the
materials and sources mentioned in the discussion section, as well as using the
results of microarray data analysis, it seems that beta-glucan in the edible
mushroom Agaricus blazei can act as a preventive by guiding the damaged liver
cells in hepatitis C patients by increasing the expression of caspase 2
protein. and even treat liver cancer.
Author contribution
All authors have equal contribution.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
1. 1. Firenzuoli F, Gori L, Lombardo G. The
medicinal mushroom Agaricus blazei murrill: Review of literature and
pharmaco-toxicological problems. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative
Medicine. 2008.
2. Mirończuk-Chodakowska
I, Kujawowicz K, Witkowska AM. Beta-glucans from fungi: Biological and
health-promoting potential in the covid-19 pandemic era. Nutrients.
2021;13(11).
3. Kobayashi H, Yoshida R,
Kanada Y, Fukuda Y, Yagyu T, Inagaki K, и съавт. Suppressing effects of daily
oral supplementation of beta-glucan extracted from Agaricus blazei Murill on
spontaneous and peritoneal disseminated metastasis in mouse model. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 2005;131(8):527–38.
4. Rahar S, Swami G,
Nagpal N, Nagpal M, Singh G. Preparation, characterization, and biological
properties of β-glucans. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2011;2(2):94.
5. Negro F. Mechanisms and
significance of liver steatosis in hepatitis C virus infection. Том 12, World
Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006. с 6756–65.
6. Hoofnagle JH. Hepatitis
C: The clinical spectrum of disease. В: Hepatology. 1997.
7. Goedert JJ, Elaine
Eyster M, Lederman MM, Mandalaki T, De Moerloose P, White GC, и съавт.
End-stage liver disease in persons with hemophilia and transfusion-associated
infections. Blood. 2002;100(5):1584–9.
8. Salari N, Kazeminia M,
Hemati N, Ammari-Allahyari M, Mohammadi M, Shohaimi S. Global prevalence of
hepatitis C in general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Том
46, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022.
9. Vigneswara V, Ahmed Z.
The Role of Caspase-2 in Regulating Cell Fate. Том 9, Cells. 2020.
10. Ho LH, Taylor R, Dorstyn
L, Cakouros D, Bouillet P, Kumar S. A tumor suppressor function for caspase-2.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(13):5336–41.
11. Shi M, Vivian CJ, Lee
KJ, Ge C, Morotomi-Yano K, Manzl C, и съавт. DNA-PKcs-PIDDosome: A Nuclear
Caspase-2-Activating Complex with Role in G2/M Checkpoint Maintenance. Cell.
2009;136(3):508–20.
12. Trevino V, Falciani F,
Barrera-Saldaña HA. DNA Microarrays: a Powerful Genomic Tool for Biomedical and
Clinical Research. Mol Med [Интернет]. 2007;13(9):527–41. Available at:
https://doi.org/10.2119/2006-00107.Trevino
13. Grinde B, Hetland G,
Johnson E. Effects on gene expression and viral load of a medicinal extract
from Agaricus blazei in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Int
Immunopharmacol. 2006;6(8):1311–4.
14. Govindarajan R, Duraiyan
J, Kaliyappan K, Palanisamy M. Microarray and its applications. J Pharm
Bioallied Sci. 2012;4(6):310.
15. Pinter M, Trauner M,
Peck-Radosavljevic M, Sieghart W. Cancer and liver cirrhosis: Implications on
prognosis and management. Том 1, ESMO Open. 2016.
16. Wong RSY. Apoptosis in
cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. Том 30, Journal of Experimental and
Clinical Cancer Research. 2011.
17. Nam JY, Jong WL, Yun JK,
Young HS, Su YK, Suk WN, и съавт. Loss of caspase-2, -6 and -7 expression in
gastric cancers. Apmis. 2004;112(6):330–5.
18. Earnshaw WC, Martins LM,
Kaufmann SH. Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Том 68, Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1999. с
383–424.
19. Olsson M, Zhivotovsky B.
Caspases and cancer. Том 18, Cell Death and Differentiation. 2011. с 1441–9.