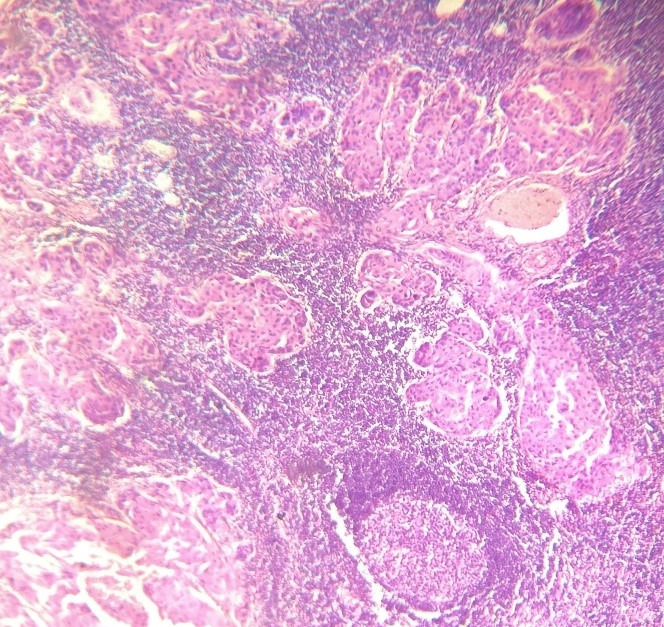
A histopathological study on breast carcinoma with special reference to cyclin-D1 and estrogen receptor
Keywords:
Breast carcinoma, Histopathological grades, Lymph node metastasis, Estrogen receptor (ER), Cyclin-D1, Menopausal statusAbstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer-related death in women in developing nations. Breast cancer diagnoses have increased as a result of rising awareness among women. The expression of Estrogen receptors (ER) plays a crucial role in determining the responsiveness to specific treatments. Cyclin D1 being a marker for cell proliferation was used in this study. The primary objectives of the current investigation were to investigate the expression of Cyclin-D1 and Estrogen receptor (ER) in breast carcinoma and to establish a relationship between the expression patterns of Cyclin-D1 and ER with the histopathological features of the tumor in breast carcinoma.
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in the Department of Pathology, Silchar Medical College and Hospital, Silchar, India, from June 2021 to May 2022. A total of 59 cases of primary breast carcinoma MRM(Modified radical mastectomy) specimens were included in the study.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 52.12 ± 12.47 years, and the majority of the patients were in the post-menopausal phase. Lymph node metastasis was observed in 47.5% of the cases, and the majority of the cases were in grade II. The study demonstrated a trend towards increased Cyclin-D1 and ER-positive with aging. Cyclin-D1 positivity decreases and Cyclin-D1 negativity increases as the tumor growth increases. The study showed a statistically significant association (P=0.001) between ER and Cyclin-D1. The majority of post-menopausal patients had ER-positive.
Conclusion: The present study provides the incidence of different parameters associated with breast carcinoma and their statistical correlation with CyclinD1 and ER that will provide improved and crucial treatment guidance.
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Payel Hazari , Monoj Kumar Deka, Bandana Kanoo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
