Effect of Satureja mutica extract on serum nitric oxide levels in rats: potential role of quercetin
Keywords:
Hydroalcoholic Extract, Satureja mutica, Nitric oxide, Male Rats, Blood LevelAbstract
Introduction: This study aimed to investigate the impact of the hydroalcoholic extract of Satureja mutica (S.mutica), a commonly used plant for cardiovascular diseases in Northern Iran, on nitric oxide levels in the blood.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into three groups, each consisting of 5 rats. The groups included a control group, a group that administered normal saline, and a group that received an extract at a dosage of 100 mg/kg. The normal saline and extract were administered through intraperitoneal injection (IP) once a day for a week. Blood samples were gathered from the heart in order to analyze the serum level of nitric oxide using spectrophotometric analysis.
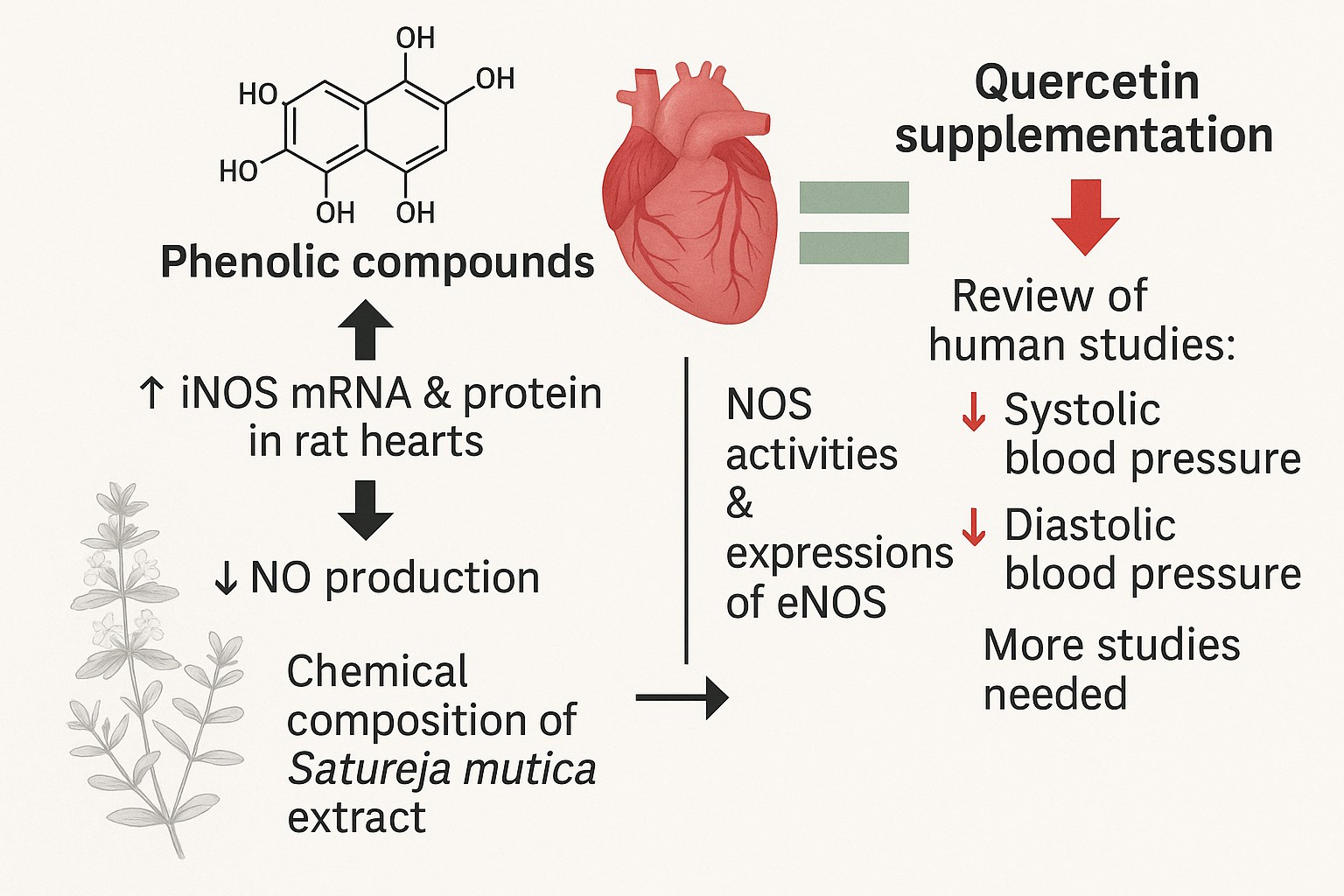
Results: The serum level of nitric oxide in the groups receiving normal saline did not change significantly compared to the control group, but the serum level of Nitric oxide decreased significantly only in the rats receiving the Satureja mutica extract compared to the control group (P<0.001). HPLC-PDA results show that the most phenolic compounds present in the extract are Gallic acid, 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid, Cinnamic Acid, Quercetin and Apigenin. The highest content and percentage of phenolic compounds is Quercetin.
Conclusions: Hydroalcoholic extract of S. mutica reduces serum NO levels in rats. Quercetin may contribute to this effect; however, confirmatory studies using isolated compounds are required. Although these findings are promising, more human studies are needed to determine whether this compound could be an alternative or complementary treatment.
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Armin Alinejad Feshposhteh, Edris Mahdavi Fikjvar, Amir Jalali

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
