Psychometric properties of the Persian avoidance-endurance questionnaire in Iranian patients with chronic non-specific low back pain: a cross-sectional
Keywords:
Low back pain, Psychometrics, Questionnaires, Test-retest reliability, Avoidance-endurance modelAbstract
Introduction: The Avoidance-Endurance Questionnaire (AEQ) is a suitable instrument for assessing pain-related endurance and avoidance responses in individuals with chronic non-specific low back pain (CNSLBP). The aim of this study was to assess of factor structure and psychometric properties of Persian version of AEQ.
Materials and Methods: The groups that were recruited in this psychometric study were 120 individuals who had history of CNSLBP of more than three months. First, the Persian AEQ factorial structure has been investigated on the basis of the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) with the Principal Axis Factoring and Promax oblique rotation method. An analysis of the usefulness of the extracted model was then performed through a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) that included bootstrapping procedures and modification indices. Moreover, test-retest reliability and internal consistency were tested to realize the stability and reliability of the factors identified.
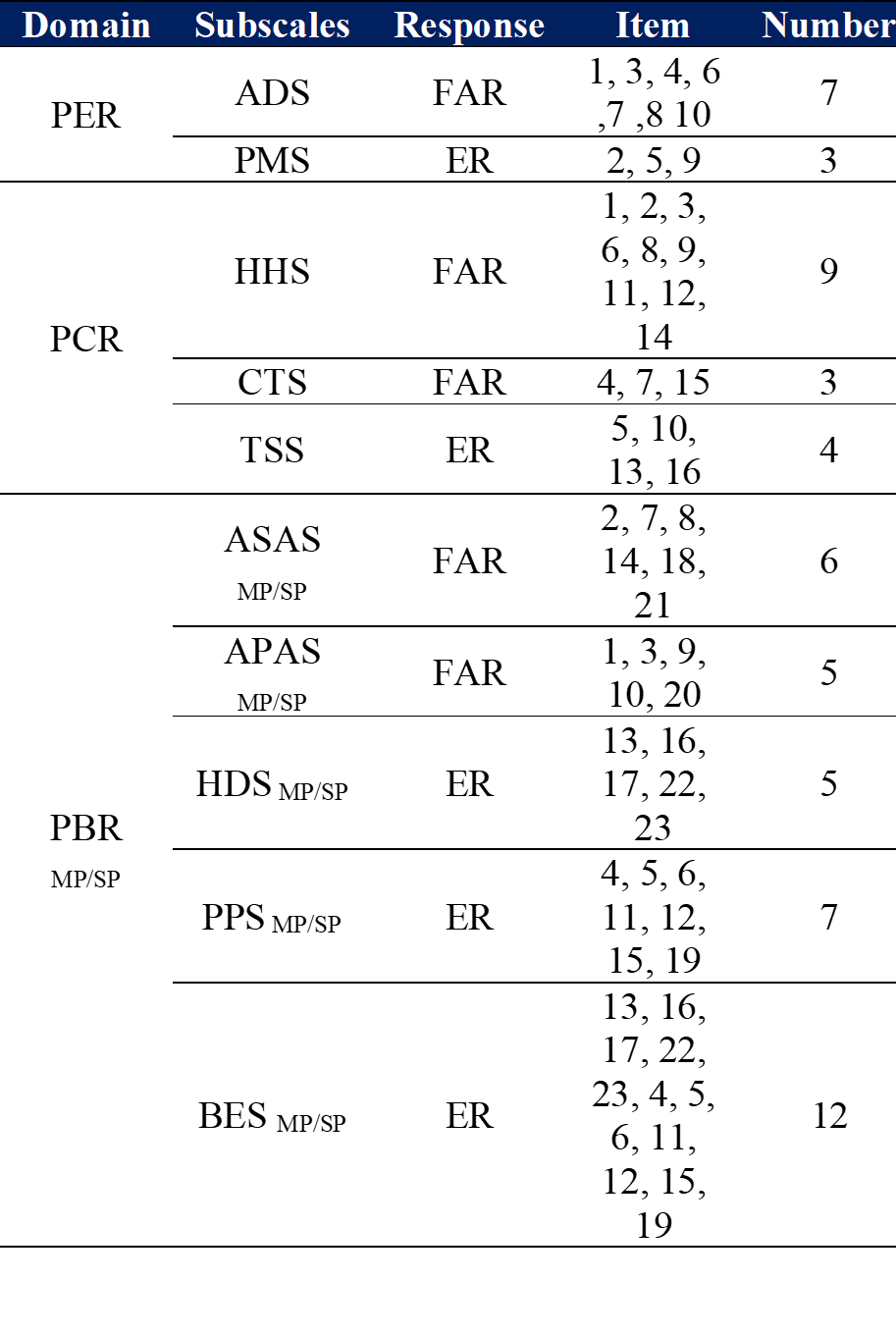
Results: The EFA demonstrated two factors in the emotional domain, three in the cognitive domain and four and three in the behavioral domain when it is mild and severe pain, respectively. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) values were between 0.76 and 0.85; Bartlett Test of Sphericity was significant (p < 0.001) which proved that the data is sufficient to conduct factor analysis. The CFA also justified the extracted structure, it was shown that the model fit indices are in the range of poor to acceptable Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) = 0.05-0.10, Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.88-0.98, and χ2/df = 1.36-2.45. Internal consistency scores varied between 0.66 and 0.91, whereas the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient varied between 0.42 and 0.83, which is satisfactory inter-dimensional reliability.
Conclusion: The AEQ Persian version eventually exhibited a nine-factor structure whose models of fit were in the range of poor to acceptable. In addition, the results connected to internal consistency, test-retest indicate the adequate psychometric characteristics and clinical validity of this version.
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sarvenaz Karimi Ghasem Abad, Behnam Akhbari , Mahyar Salavati, Ahmad Saeedi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
