Practical application of stem cell therapy in retinoblastoma
Keywords:
Retinoblastoma, Stem cell, Therapy, Translational elementsAbstract
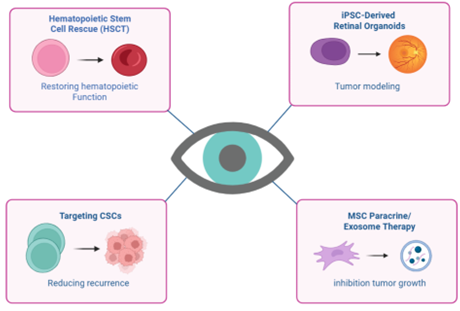
Retinoblastoma (RB), recognized as the most prevalent intraocular malignancy in pediatric populations, continues to pose considerable therapeutic challenges due to its genetic etiology, tumor heterogeneity, and resistance to standard treatment modalities. Recent progress in stem cell biology has introduced innovative approaches for both disease modeling and therapeutic intervention. The utilization of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and retinal organoids has enabled the in vitro recapitulation of retinal development and RB pathogenesis, thereby facilitating precision drug screening and elucidation of underlying mechanisms. Additionally, the identification of cancer stem cells (CSCs) within RB has redirected therapeutic strategies toward targeting pathways involved in self-renewal, mechanisms of drug resistance, and tumor propagating cells, to prevent relapse and metastasis. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as promising vectors for tumor-targeted therapy, leveraging paracrine effects and exosome-mediated delivery of therapeutic agents, thus offering minimally invasive and systemic approaches to overcoming drug resistance and modulating tumor behavior. Furthermore, hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) rescue has improved the safety profile of high-dose chemotherapy regimens by mitigating treatment-associated toxicities. Collectively, these stem cell-based strategies underscore the multifaceted role of cellular therapies in RB, heralding a future characterized by integrated, personalized, and less invasive therapeutic modalities.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Elahe Bakhshalipour, Ali Najafizadeh, Majid Mirmazloumi, Parisa Hamami Shirzy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
