Alzheimer’s disease and glioblastoma: a comprehensive review of epidemiological and translational medicine
Keywords:
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Glioblastoma, Neuropsychiatric disorders, Genetic risk factorsAbstract
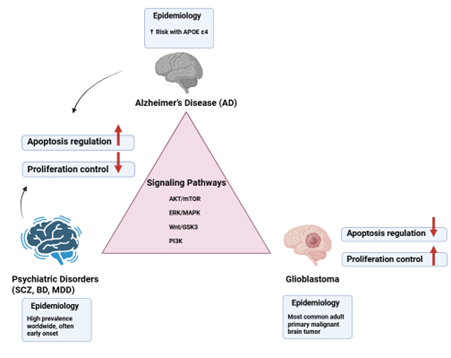
Alzheimer's disease (AD), neuropsychiatric disorders, and glioblastoma represent distinct yet interconnected conditions characterized by overlapping molecular, cellular, and genetic mechanisms. Epidemiological studies reveal an inverse comorbidity between AD and glioblastoma, while psychiatric disorders may influence glioblastoma susceptibility through genetic, cellular, and pharmacological factors. Consequently, numerous critical signaling pathways, such as protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (AKT/mTOR), extracellular signal-regulated kinase / mitogen-activated protein Kinase (ERK/MAPK), wingless-related integration Site/glycogen synthase kinase 3 (Wnt/GSK3), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), exhibit dysregulation across these conditions, affecting apoptosis, proliferation, and synaptic function. In addition, genetic risk factors, including apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 (APOE ε4) in AD and tumor protein 53 (TP53), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/2) in glioblastoma, play a role in shaping divergent disease trajectories. Neuroinflammatory processes, epigenetic changes, and interactions between neurons and glia further clarify susceptibility patterns. From a therapeutic perspective, repurposing psychiatric medications that target common molecular pathways and implementing epigenetic or gene-based interventions offer promising avenues for integrated treatment strategies. This review aims to synthesize the current understanding of the epidemiological, molecular, cellular, and genetic intersections among AD, psychiatric disorders, and glioblastoma.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ali Najafizadeh, Elahe Bakhshalipour, Maryam Gholamniya Foumani, Majid Mirmazloumi, Mohsen Safi Samgh Abadi, Zohreh Teymori

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
